views
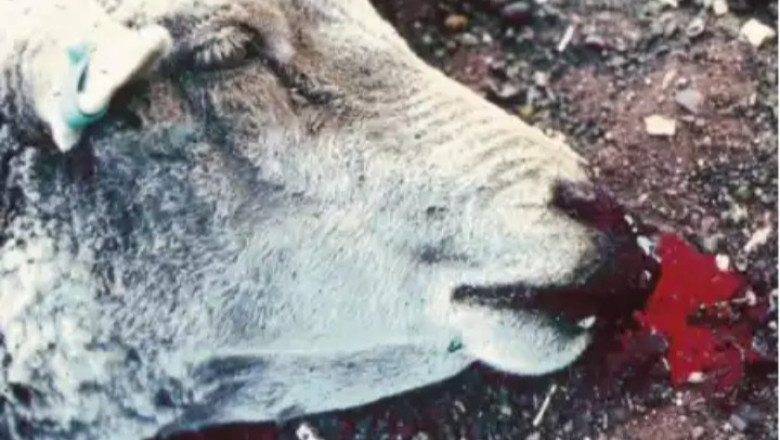

1. Animal experiencing bleeding without blood clot
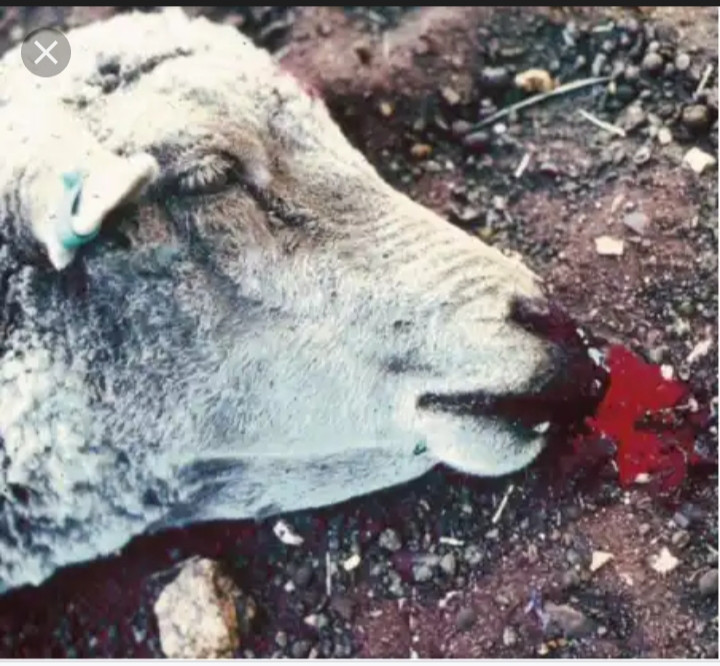
The Federal Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development (FMARD) in a recent release has confirm the outbreak of Anthrax disease in a farm located in Niger state Nigeria, this outbreak was recorded in a farm where livestock are raised following the outbreak of Anthrax disease in West Africa which was first reported in Ghana on the 13th day of July 2023, the outbreak was confirm after report was made following the sudden deaths of livestock in a farm with eight (8) mortality and it was observed that these animals experienced bleeding from external orifices without blood clotting.
Following this report, samples were collected on 14th day of July 2023 from multiple species in this livestock farm and transported to the National Veterinary Research Institute (NVRI), VOM, Plateau State for testing and the results tested positive to the disease. Currently investigation is ongoing to trace the source of these infection and identify its spreads. With human exposure recorded to have taken place without any positive symptoms recorded. The FMARD and the Nigeria Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (NCDC) are currently working closely with the Niger State Ministries of Health and Agriculture to identify, isolate and follow up all exposed persons. The NCDC has activated the incident management system (IMS) at level two (2) today with an incident manager appointed for effective coordination of the response. The risk assessment conducted by the human health sector today remained high for the likelihood of an outbreak and its potential impact on humans.
What is Anthrax Disease?
Anthrax is an infectious disease caused by a rod-shaped gram-positive bacteria known as Bacillus anthracis. It occurs naturally in soil and commonly affects domestic and wild animals around the world. Humans can also host this bacteria when they come in contact with infected animals or contaminated animal products. Anthrax can lead to severe illness in both humans and animals
Things to know about this disease
Is Anthrax Disease contagious? Anthrax disease is not contagious like cold or flu but can be contacted by humans when spores gets into their bodies. These bacterial produces spores which can remain dormant for years until they find their way into the body of a host, once ingested the spores are activated and these bacteria begin to reproduce.
Common hosts for anthrax include wild or domestic livestock, such as sheep, cattle, horses, goats and sometimes humans. When these spores gets into the body of the host they become active, begin to multiply, spread to other parts and produces toxins which can cause severe illness to their hosts.
How then do these spores get into the body of humans?
This can happen when people breathe in spores, eat food or drink water which are contaminated with these bacterial, or when spores come into contact with open wounds or scrape in the skin.
Symptoms of anthrax infection
Anthrax in animals can cause the following symptoms such as high fever, bleeding from all body openings (nose, mouth, ears, anus etc.), joint weakness, loss of appetite, swelling on skin, experiencing difficulty while breathing, bloody diarrhea, It can lead to sudden death in most cases. Animals infected with Anthrax do not have blood clot when it is exposed to air.In humans Anthrax can display its symptoms depending on the method of its infection, its routes may differs so also the symptoms experienced, anthrax can cause fever, painless skin sores with a black Centre that appears after the blisters, general body weakness and also difficulty in breathing. It can also cause severe digestive illness that poses itself as food poisoning.
How to prevent this disease?
1. Farmers should ensure they wear nitrile and gloves to prevent skin contact with contaminated animals, materials and surfaces.
2. Farmers should ensure they use eyes, face and respiratory protection kits when going into rooms where infected animals are kept
3. Farm owners in prone regions with history of Anthrax should get theirs livestock vaccinated yearly to prevent future infestation.
4. Infected animals should be separated from the others and quarantine
5. Proper carcass disposal should be carried out to prevent environmental contamination and further spread.
What to do when you feel at risk with Anthrax
If you feel exposed to this bacterial ensure you seek medical attention to receive antibiotic PEP for 7 days and also have your symptoms monitored for14 days.












Comments
0 comment